Softspec lecture 4 - 12 February 2015
(Note: stuff in slide may not be noted here)
Use case & Re-engineering
Many companies has legacy code. Maybe the documentation is not good and the maintainer left.
To work with them, we might have to redevelop them or re-engineer it.
To re-engineer contains two phases
- Reverse engineer: look at working application and see models out of it
- Look at the code quality
- How much we should re-engineer it? (maybe the code can't be be run any more)
- Worst case: use the knowledge from it to start from the group up
- Build the abstract model (Mostly in inception, elaboration phase of UP) because the code could be quite large
- One way to do this: interview users
- But the users doesn't know how exactly the code works
- Then we get use cases
- Analysis the implementation model
- Look at packages, folders, files, etc.
- Run the use cases
- Record the method calls ("traces")
- Trace is not complete! It depends on input and environment (eg. if method branches depending on output of
Math.random())
- Map function to the implementation model
- Now we should have an idea where to start your work
- Forward engineer: think about future development
User story
- Originated from Extreme Programming
- Tell you what users want
- More lightweight than use cases
- Use case is sequential
- User story CANNOT be changed
- Short (1-2 sentences)
- Self contained
- Answer who/what/why
Cons:
- User story can't scale very well
- We have to keep track every of them and there're a lot of them
- Compared to use case it contains multiple user stories into one flow
- Doesn't contain non functional requirements
Examples:
- As a something, I want something so that something
- As a cashier, I want to see a list of products customer is purchasing so that I can tell the customer how much they have to pay
- Maybe omit the benefit?
- As a cashier, I want to see a list of products customer is purchasing
- Or even emphasize it
- To tell the customer how much they have to pay, as a cashier I want to see a list of products customer is purchasing
Elaboration
- Implement simple, key version of the application
- Don't implement all requirements at once
- Mostly focus at 1 use case in each iteration (but could be more)
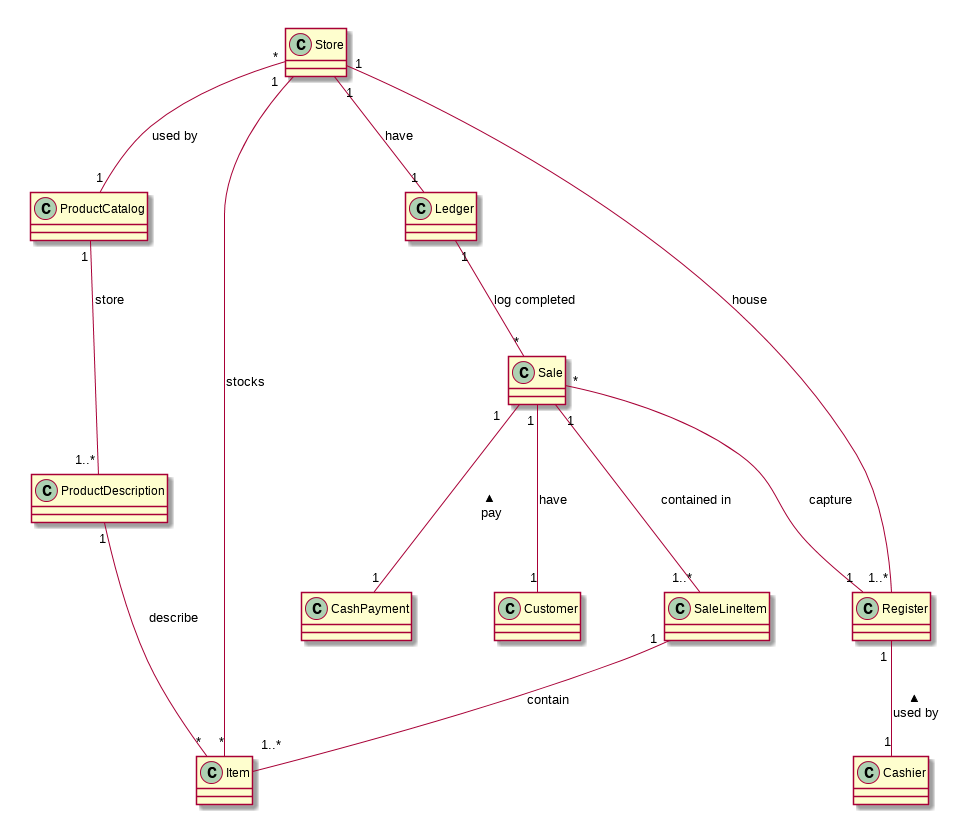
Domain model
- We write domain model because it help you see relationship between objects and business people would understand application better
- Number, text, boolean should be attribute in domain model
- But something bigger like "Airport" (that has its name, code, etc) should be class.
Sale