Softspec Lecture 5 - 19 February 2015
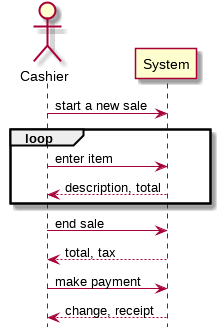
System Sequence Diagram (SSD)
- SSD shows a single sequence of use case
- Show the sequence of interaction between model objects
- Objects and interactions should be named at the abstract level (goal, intend not UI)
- No activation boxes
Use case
- Customer arrives at POS with items
- Cashier starts at a new sale
- Cashier enters item id
- System records sale line item and present item description, price and total
- Cashier repeats step 3-4 until done
- System present total with taxes calculated
- Cashier tells customer the total and ask for payment
- Customer pay and system handle payment
Operational Contract
- Precondition, postcondition
- Write postcondition in past tense
- A
SaleLineItemwas created - NO Create a
SaleLineItem - no A
SaleLineItemis created
Example
Contract CO2: enterItem
- Operation: enterItem(itemID : ItemID, quantity : Integer)
- Cross References: Use Cases: Process Sale
- Preconditions: There is a sale underway (what should happen before this operation)
- Postconditions:
- A
SaleLineItemsliinstance was created sliwas associated with the currentSalesli.quantitybecame quantity
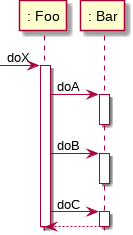
Sequence diagram
- How objects interact with messages
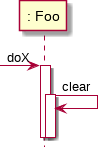
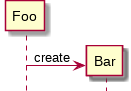
Notation
Message
self call
creation
termination
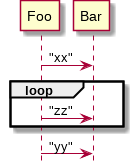
loop
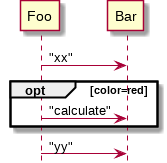
condition
reference
Communication diagram
- Same as interaction diagram but more compact
- PlantUML can't draw it so no picture in this lecture note :(
Class diagram
- Static object modelling
- Don't put both relationship and attribute of the same thing.
- If attribute is a data type it should be put as attribute
- If attribute is another object it should be put in another related class
- Some association are excluded in the domain model (eg. sale doesn't know register, but register know the sale it's being created)
- Use [1..*] after the attribute for collection attribute (or use a relationship line)
- Use dotted line to indicate dependency (a class cannot exists without its dependencies)
- Can add user-defined sections (eg. exception thrown, responsibilities)